| Share Presentation: https://NeoK12.com/pres/ZSOUND01 | |
Wave Basics and Sound
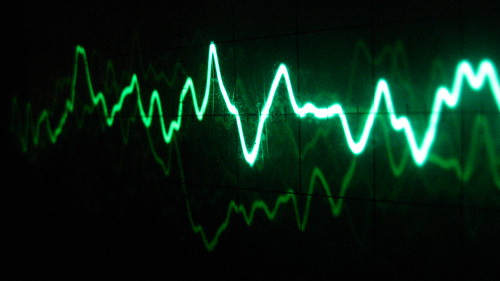
| Wave- a disturbance that transfers energy from place to place. Caption: Picture of a sound wave. Amplitude- The maximum distance the particles of a medium move away from their rest positions as a wave passes through the medium. Wavelength- The distance between the crest of one wave and the crest of the next. Caption: In this picture, the waves are moving away from each other. Frequency- The number of complete waves that pass a given point in a certain amount of time. | ||||
| Medium- material through which a wave travels. Caption: This is fire and water. Both are mediums. The other medium is a solid. | ||||
| Mechanical Wave- a wave that requires a medium through which to travel. Caption: This sign is metal. Metal is solid, and solid is a medium. A mechanical wave needs a medium to pass through. | ||||
| Transverse Wave- A wave that moves the medium in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. Caption: This is a picture of something perpendicular. As the definition says, a transverse wave moves the medium in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. Crest- The highest part of a transverse wave. Trough- The lowest part of a transverse wave. | ||||
| Longitudinal Wave- A wave that moves the medium parallel to the direction in which the wave travels. Compression- The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together. Rarefaction- The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are far apart. | ||||
| Surface Wave- A wave that occurs at the surface between two mediums. Caption: This is a wave on the surface of the water. | ||||
| Hertz (Hz)- Unit of measurement for frequency. Caption: This is a cart with measures of frequency, or Hertz. | ||||
Share this Presentation: https://NeoK12.com/pres/ZSOUND01 NeoK12.com - Educational Videos, Lessons, Quizzes & Presentations
NeoK12.com - Educational Videos, Lessons, Quizzes & Presentations
All images are linked from Flickr Creative Commons under CC BY, CC BY-SA, CC0. Click attribution link under image for full details.