| Share Presentation: https://NeoK12.com/pres/ZGENETC1 | |
|
| ||||
|
In genetics a feature of a living thing is called a "trait"
| ||||
|
Some traits are inherited through our genes:
| |||||
|
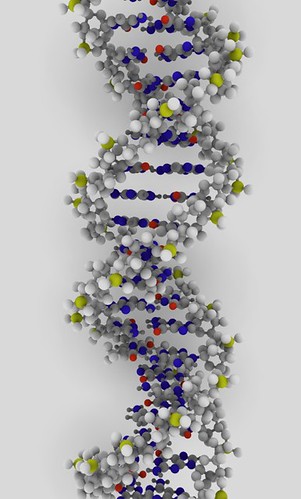
Genes are made from a long molecule called DNA.
1. DNA is copied and inherited across generations so we have traits similar to our parents. 2. The order of these units carries genetic information, similar to how the order of letters on a page carries information. 3. This information is the instructions for constructing and operating a living organism. 4. Different copies of a gene do not always give exactly the same instructions 5. Each unique form of a single gene is called an allele. 6. As an example, one allele for the gene for hair color could instruct the body to produce a lot of pigment, producing black hair. 7. A different allele of the same gene might give instructions that fail to produce any pigment, giving white hair. 8. As a second example, one allele of the eye-color gene produces green eyes and another allele of the eye-color gene produces brown eyes. | ||||
|
How Do I Get My Parents Traits?
| |||||
|
Why is my hair not red like my fathers?
| |||||